NRP: 05111740000097
Kelas: PBO-A
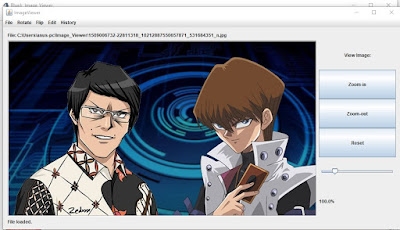
1. Rancangan Interface Editor
2. Definisi Class
Class ImageViewer : Kelas utama dari Image Viewer
Class OFImage : Kelas yangmendefinisikan gambar dalam format Object First(OF)Class ImagePanel : Kelas komponen swing yang menampilkan OFImage
Class ImageFileManager : Kelas untuk memuat dan menyimpan gambar
Class Filter : abstrak untuk semua filter gambar
Class FlipVertically Filter : membalikkan gambar
Class Lighter Filter : membuat filter lighter
Class Pixelize Filter : membuat filter pixel
Class Darker Filter : membuat filter darker
Class Threshold Filter : membuat filter threshold
Class Solarize Filter : membuat filter solarize
Class Edge Filter : membuat filter edge
Class Invert Filter : membuat filter invert
Class Mirror Filter : membuat filter mirror
Class Smooth Filter : membuat filter smooth
Class Gray Scale Filter : membuat filter gray scale
3. Berikut source code masing-masing class
A) Class ImageViewer
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.*;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeEvent;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeListener;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ImageViewer
{
// static fields:
private static JFileChooser fileChooser = new JFileChooser(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
private static final String DEGREE = "\u00b0";
// fields:
private JFrame frame;
private ImagePanel imagePanel;
private JLabel filenameLabel;
private JLabel statusLabel;
private OFImage currentImage;
private JScrollPane scrollPanel;
private JLabel zoomLabel;
private JButton zoomInButton;
private JButton zoomOutButton;
private JButton zoomReset;
private JSlider zoomSlider;
private JLabel zoomValue;
private JFrame scFrame;
private JSpinner spinnerW;
private JSpinner spinnerH;
private JLabel sizeLabel1;
private JLabel sizeLabel2;
private JButton sizeOK;
private JButton sizeCancel;
private JCheckBox sizeRatio;
private HistoryManager historyMan;
private JFrame rFrame;
private JSlider rotateSlider;
private JLabel rotateDegrees;
private JButton rotateOK;
boolean click;
boolean changedH;
boolean changedW;
double zoom=100;
private List<Filter> filters;
/** Create an ImageViewer and display its GUI on screen.
*/
public ImageViewer()
{
currentImage = null;
historyMan= new HistoryManager();
filters = createFilters();
makeFrame();
zoom=100;
deactivateButtons();
}
// ---- implementation of menu functions ----
/**
Open File
*/
private void openFile()
{
int returnVal = fileChooser.showOpenDialog(frame);
if(returnVal != JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) {
return; // cancelled
}
File selectedFile = fileChooser.getSelectedFile();
currentImage = ImageFileManager.loadImage(selectedFile);
if(currentImage == null) { // image file was not a valid image
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(frame,
"The file was not in a recognized image file format.",
"Image Load Error",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
historyMan.eraseAll();
historyMan.add(currentImage);
imagePanel.setImage(currentImage);
imagePanel.saveOriginal();
showFilename(selectedFile.getPath());
showStatus("File loaded.");
frame.pack();
Dimension d = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
frame.setLocation(d.width/2 - frame.getWidth()/2, d.height/2 - frame.getHeight()/2);
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
activateButtons();
resetSlider();
}
/** close image */
private void close()
{
currentImage = null;
imagePanel.clearImage();
showFilename(null);
deactivateButtons();
resetSlider();
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
historyMan.eraseAll();
}
/** Save Image*/
private void saveAs()
{
if(currentImage != null) {
int returnVal = fileChooser.showSaveDialog(frame);
if(returnVal != JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) {
return; // cancelled
}
File selectedFile = fileChooser.getSelectedFile();
ImageFileManager.saveImage(currentImage, selectedFile);
showFilename(selectedFile.getPath());
}
}
/**Quit*/
private void quit()
{
System.exit(0);
}
/**Apply a filter to image.*/
private void applyFilter(Filter filter)
{
if(currentImage != null) {
OFImage filtered =new OFImage(currentImage);
filter.apply(filtered);
showStatus("Applied: " + filter.getName());
currentImage=filtered;
imagePanel.setImage(currentImage);
imagePanel.saveOriginal();
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
historyMan.add(currentImage);
frame.repaint();
}
else {
showStatus("No image loaded.");
}
}
/**Repaints main frame*/
private void refreshFrame(){
frame.repaint();
}
/**
* Create a list of filters.
*/
private List<Filter> createFilters()
{
List<Filter> filterList = new ArrayList<Filter>();
filterList.add(new DarkerFilter("Darker"));
filterList.add(new LighterFilter("Lighter"));
filterList.add(new GrayScaleFilter("Grayscale"));
filterList.add(new ThresholdFilter("Threshold"));
filterList.add(new SmoothFilter("Smooth"));
filterList.add(new InvertFilter("Invert"));
filterList.add(new SolarizeFilter("Solarize"));
filterList.add(new PixelizeFilter("Pixelize"));
filterList.add(new EdgeFilter("Edge Detection"));
return filterList;
}
/**
* Resize function
*/
private void resize(int newWidth, int newHeight){
BufferedImage resized = new BufferedImage(newWidth, newHeight, currentImage.getType());
Graphics2D g = resized.createGraphics();
g.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_INTERPOLATION,
RenderingHints.VALUE_INTERPOLATION_BILINEAR);
g.drawImage(currentImage, 0, 0, newWidth, newHeight, 0, 0, currentImage.getWidth(),
currentImage.getHeight(), null);
g.dispose();
OFImage img = new OFImage(resized);
currentImage=img;
imagePanel.setImage(currentImage);
imagePanel.saveOriginal();
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
historyMan.add(currentImage);
showStatus("Image resized");
}
/**Zoom Image*/
private void zoomInBy10(){
imagePanel.zoom(zoom+10);
zoom=zoom+10;
}
private void zoomOutBy10(){
imagePanel.zoom(zoom-10);
zoom=zoom-10;
}
private void zoomByFactor(int fact){
imagePanel.zoom(fact);
zoom=fact;
}
/**
* Rotate Image
*/
private void rotate(int angle){
if (currentImage!=null)
{
double sin = Math.abs(Math.sin(Math.toRadians(angle)));
double cos = Math.abs(Math.cos(Math.toRadians(angle)));
int w = currentImage.getWidth();
int h = currentImage.getHeight();
int neww = (int) Math.floor(w*cos + h*sin);
int newh = (int) Math.floor(h*cos + w*sin);
BufferedImage rotated = new BufferedImage(neww, newh, currentImage.getType());
Graphics2D g = rotated.createGraphics();
g.translate((neww-w)/2, (newh-h)/2);
g.rotate(Math.toRadians(angle), w/2, h/2);
g.drawImage(currentImage,null,0,0);
g.dispose();
currentImage=new OFImage(rotated);
imagePanel.setImage(currentImage);
imagePanel.saveOriginal();
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
historyMan.add(currentImage);
showStatus("Rotated by "+angle+DEGREE);
}
else
showStatus("No image loaded!");
}
/**
* Activating, deactivating and resetting buttons/sliders
*/
private void deactivateButtons(){
zoomInButton.setEnabled(false);
zoomOutButton.setEnabled(false);
zoomReset.setEnabled(false);
zoomSlider.setEnabled(false);
}
private void activateButtons(){
zoomInButton.setEnabled(true);
zoomOutButton.setEnabled(true);
zoomReset.setEnabled(true);
zoomSlider.setEnabled(true);
}
private void resetSlider(){
click=true;
zoomSlider.setValue(100);
zoom=100;
zoomValue.setText(""+zoom+"%");
}
// ---- support methods ----
/**
* Show the file name of the current image in the fills display label.
*/
private void showFilename(String filename)
{
if(filename == null) {
filenameLabel.setText("No file.");
}
else {
filenameLabel.setText("File: " + filename);
}
}
/**
* Show a message
*/
private void showStatus(String text)
{
statusLabel.setText(text);
}
// ---- Swing stuff to build the frame and all its components and menus ----
/**
* Create the Swing frame and its content.
*/
private void makeFrame()
{
frame = new JFrame("ImageViewer");
JPanel contentPane = (JPanel)frame.getContentPane();
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(12, 12, 12, 12));
makeMenuBar(frame);
// Specify the layout manager with nice spacing
contentPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout(6, 6));
// Create the image pane with scroll panes in the center
imagePanel = new ImagePanel();
scrollPanel = new JScrollPane(imagePanel);
scrollPanel.setBorder(new EtchedBorder());
contentPane.add(scrollPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
// Create two labels at top and bottom for the file name and status messages
filenameLabel = new JLabel();
contentPane.add(filenameLabel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
statusLabel = new JLabel();
contentPane.add(statusLabel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
//Create a panel with two buttons, a slider and a label for zooming on right
JPanel zoomPanel=new JPanel();
zoomPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(0,1));
zoomLabel = new JLabel("View Image:");
zoomLabel.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
zoomLabel.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.CENTER);
zoomPanel.add(zoomLabel);
zoomInButton = new JButton("Zoom-in");
zoomInButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if ((zoom>=10)&&(zoom<=490)){
click=true;
zoomInBy10();
zoomValue.setText(""+(zoom)+"%");
zoomSlider.setValue(zoomSlider.getValue()+10);
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
}
}
});
zoomPanel.add(zoomInButton);
zoomOutButton = new JButton("Zoom-out");
zoomOutButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if ((zoom>=20)&&(zoom<=500)){
click=true;
zoomOutBy10();
zoomValue.setText(""+(zoom)+"%");
zoomSlider.setValue(zoomSlider.getValue()-10);
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
}
}
});
zoomPanel.add(zoomOutButton);
zoomReset=new JButton("Reset");
zoomReset.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
click=true;
zoomByFactor(100);
zoomValue.setText(""+(zoom)+"%");
zoomSlider.setValue(100);
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
}
});
zoomPanel.add(zoomReset);
zoomSlider= new JSlider(10,500,100);
zoomSlider.addChangeListener(new ChangeListener() {
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
if(click){
click=false;
}
else{
zoomByFactor(zoomSlider.getValue());
zoomValue.setText(""+zoom+"%");
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
}
}
});
zoomPanel.add(zoomSlider);
zoomValue= new JLabel(""+zoom+"%");
zoomPanel.add(zoomValue);
contentPane.add(zoomPanel, BorderLayout.EAST);
// building is done - arrange the components
showFilename(null);
frame.pack();
// place the frame at the center of the screen and show
Dimension d = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
frame.setLocation(d.width/2 - frame.getWidth()/2, d.height/2 - frame.getHeight()/2);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
/**
* Create the main frame's menu bar.
*
* @param frame The frame that the menu bar should be added to.
*/
private void makeMenuBar(JFrame frame)
{
final int SHORTCUT_MASK =
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getMenuShortcutKeyMask();
JMenuBar menubar = new JMenuBar();
frame.setJMenuBar(menubar);
JMenu menu;
JMenuItem item;
// create the File menu
menu = new JMenu("File");
menubar.add(menu);
item = new JMenuItem("Open...");
item.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_O, SHORTCUT_MASK));
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { openFile(); }
});
menu.add(item);
item = new JMenuItem("Close");
item.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_W, SHORTCUT_MASK));
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { close(); }
});
menu.add(item);
menu.addSeparator();
item = new JMenuItem("Save As...");
item.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_S, SHORTCUT_MASK));
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { saveAs(); }
});
menu.add(item);
menu.addSeparator();
item = new JMenuItem("Quit");
item.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_Q, SHORTCUT_MASK));
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { quit(); }
});
menu.add(item);
//create Rotate menu
menu=new JMenu("Rotate");
menubar.add(menu);
item = new JMenuItem("Rotate by 90 Right");
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
rotate(90);
}
});
menu.add(item);
item = new JMenuItem("Rotate by 90 Left");
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
rotate(-90);
}
});
menu.add(item);
item = new JMenuItem("Rotate by....");
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
makeRotateFrame();
}
});
menu.add(item);
// create the Flip menu
menu = new JMenu("Flip");
menubar.add(menu);
item = new JMenuItem("Flip horizontally");
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
applyFilter(new MirrorFilter("Flip horizontally"));
}
});
menu.add(item);
item=new JMenuItem("Flip vertically");
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
applyFilter(new FlipVerticallyFilter("Flip vertically"));
}
});
menu.add(item);
// create the Filter menu
menu = new JMenu("Edit");
menubar.add(menu);
item = new JMenuItem("Change size");
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
makeSizeChangeFrame();
}
});
menu.add(item);
for(final Filter filter : filters) {
item = new JMenuItem(filter.getName());
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
applyFilter(filter);
}
});
menu.add(item);
}
/*Create History*/
menu = new JMenu("History");
menubar.add(menu);
item=new JMenuItem("Undo");
item.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_Z, SHORTCUT_MASK));
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
historyMan.undo();
OFImage img=historyMan.getCurrentVersion();
currentImage=img;
imagePanel.setImage(img);
imagePanel.saveOriginal();
refreshFrame();
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
}
});
menu.add(item);
item=new JMenuItem("Redo");
item.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_Y, SHORTCUT_MASK));
item.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
historyMan.redo();
OFImage img=historyMan.getCurrentVersion();
currentImage=img;
imagePanel.setImage(img);
imagePanel.saveOriginal();
refreshFrame();
scrollPanel.getViewport().revalidate();
}
});
menu.add(item);
}
private void makeSizeChangeFrame(){
if(currentImage!=null){
scFrame=new JFrame("Change image size");
JPanel contentPane = (JPanel)scFrame.getContentPane();
contentPane.setLayout(new GridLayout(0,3,10,5));
//Creates a spinner with text forms and labels for changing picture size
sizeLabel1= new JLabel("Width:");
contentPane.add(sizeLabel1);
int height=currentImage.getHeight();
int width=currentImage.getWidth();
spinnerW=new JSpinner(new SpinnerNumberModel(width,1,4000,1));
spinnerW.addChangeListener(new ChangeListener() {
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent arg0) {
if (changedH){
changedH=false;
return;
}
if(sizeRatio.isSelected()){
click=true;
double ratio=new Double(currentImage.getWidth())/
new Double(currentImage.getHeight());
double newHeight=((Integer)spinnerW.getValue())/ratio;
int newVal=new Double(newHeight).intValue();
spinnerH.setValue(newVal);
changedW=true;
}
}
});
contentPane.add(spinnerW);
sizeOK=new JButton("OK");
sizeOK.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int newW=(Integer)spinnerW.getValue();
int newH=(Integer)spinnerH.getValue();
resize(newW,newH);
scFrame.dispose();
}
});
contentPane.add(sizeOK);
sizeLabel2=new JLabel("Height:");
contentPane.add(sizeLabel2);
spinnerH=new JSpinner(new SpinnerNumberModel(height,1,4000,1));
spinnerH.addChangeListener(new ChangeListener() {
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
if (changedW){
changedW=false;
return;
}
if(sizeRatio.isSelected()){
click=true;
double ratio=new Double(currentImage.getWidth())
/ new Double(currentImage.getHeight());
double newWidth=((Integer)spinnerH.getValue())*ratio;
int newVal=new Double(newWidth).intValue();
spinnerW.setValue(newVal);
changedH=true;
}
}
});
contentPane.add(spinnerH);
sizeCancel=new JButton("Cancel");
sizeCancel.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
scFrame.dispose();
}
});
contentPane.add(sizeCancel);
JPanel empty=new JPanel();
contentPane.add(empty);
sizeRatio= new JCheckBox("Constrain proportion", true);
contentPane.add(sizeRatio);
Dimension d = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
scFrame.setLocation(d.width/2 - frame.getWidth()/2, d.height/2 - frame.getHeight()/2);
scFrame.pack();
scFrame.setVisible(true);
}
else
showStatus("No image loaded");
}
private void makeRotateFrame(){
if (currentImage!=null){
rFrame=new JFrame("Rotate by degrees");
JPanel contentPane = (JPanel)rFrame.getContentPane();
contentPane.setLayout(new GridLayout(0,3,10,5));
rotateSlider=new JSlider(0,360,0);
rotateSlider.addChangeListener(new ChangeListener() {
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
rotateDegrees.setText(""+rotateSlider.getValue()+DEGREE);;
}
});
contentPane.add(rotateSlider);
rotateDegrees=new JLabel(""+rotateSlider.getValue()+DEGREE);
contentPane.add(rotateDegrees);
rotateOK=new JButton("Apply");
rotateOK.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int degrees=rotateSlider.getValue();
rotate(degrees);
rFrame.dispose();
}
});
contentPane.add(rotateOK);
Dimension d = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
rFrame.setLocation(d.width/2 - frame.getWidth()/2, d.height/2 - frame.getHeight()/2);
rFrame.pack();
rFrame.setVisible(true);
}
else
showStatus("No image loaded");
}
}
B) OFImage
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
/**
* OFImage is a class that defines an image in OF (Objects First) format.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public class OFImage extends BufferedImage
{
/**
* Create an OFImage copied from a BufferedImage.
* @param image The image to copy.
*/
public OFImage(BufferedImage image)
{
super(image.getColorModel(), image.copyData(null),
image.isAlphaPremultiplied(), null);
}
/**
* Create an OFImage with specified size and unspecified content.
* @param width The width of the image.
* @param height The height of the image.
*/
public OFImage(int width, int height)
{
super(width, height, TYPE_INT_RGB);
}
/**
* Set a given pixel of this image to a specified color. The
* color is represented as an (r,g,b) value.
* @param x The x position of the pixel.
* @param y The y position of the pixel.
* @param col The color of the pixel.
*/
public void setPixel(int x, int y, Color col)
{
int pixel = col.getRGB();
setRGB(x, y, pixel);
}
/**
* Get the color value at a specified pixel position.
* @param x The x position of the pixel.
* @param y The y position of the pixel.
* @return The color of the pixel at the given position.
*/
public Color getPixel(int x, int y)
{
int pixel = getRGB(x, y);
return new Color(pixel);
}
}
C) ImagePanel
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.image.*;
/**
* An ImagePanel is a Swing component that can display an OFImage.
* It is constructed as a subclass of JComponent with the added functionality
* of setting an OFImage that will be displayed on the surface of this
* component.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class ImagePanel extends JComponent
{
// The current width and height of this panel
private int width, height;
// An internal image buffer that is used for painting. For
// actual display, this image buffer is then copied to screen.
private OFImage panelImage;
//Saved copy of an original size image (filters are applied) - used for zooming
private BufferedImage original;
/**
* Create a new, empty ImagePanel.
*/
public ImagePanel()
{
width = 360; // arbitrary size for empty panel
height = 240;
panelImage = null;
original = null;
}
/**
* Set the image that this panel should show.
*
* @param image The image to be displayed.
*/
public void setImage(OFImage image)
{
if(image != null) {
width = image.getWidth();
height = image.getHeight();
panelImage = image;
repaint();
}
}
/**
* Saves original images, gets called after opening new image
*/
public void saveOriginal(){
original=(OFImage) panelImage;
}
/**
* Clear the image on this panel.
*/
public void clearImage()
{
Graphics imageGraphics = panelImage.getGraphics();
imageGraphics.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
imageGraphics.fillRect(0, 0, width, height);
width=360;
height=240;
repaint();
}
/**
* creates a resized instance of the original picture and displays it
* @param factor
*/
public void zoom(double factor){
double k=(factor)/100;
int newWidth = new Double(original.getWidth() * k).intValue();
int newHeight = new Double(original.getHeight() * k).intValue();
BufferedImage resized = new BufferedImage(newWidth, newHeight, original.getType());
Graphics2D g = resized.createGraphics();
g.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_INTERPOLATION,
RenderingHints.VALUE_INTERPOLATION_BILINEAR);
g.drawImage(original, 0, 0, newWidth, newHeight, 0, 0, original.getWidth(),
original.getHeight(), null);
g.dispose();
OFImage img = new OFImage(resized);
setImage(img);
}
// The following methods are redefinitions of methods
// inherited from superclasses.
/**
* Tell the layout manager how big we would like to be.
* (This method gets called by layout managers for placing
* the components.)
*
* @return The preferred dimension for this component.
*/
public Dimension getPreferredSize()
{
return new Dimension(width, height);
}
/**
* This component needs to be redisplayed. Copy the internal image
* to screen. (This method gets called by the Swing screen painter
* every time it want this component displayed.)
*
* @param g The graphics context that can be used to draw on this component.
*/
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Dimension size = getSize();
g.clearRect(0, 0, size.width, size.height);
if(panelImage != null) {
g.drawImage(panelImage, 0, 0, null);
}
}
}
D) ImageFileManager
import java.awt.image.*;
import javax.imageio.*;
import java.io.*;
/**
* ImageFileManager is a small utility class with static methods to load
* and save images.
*
* The files on disk can be in JPG or PNG image format. For files written
* by this class, the format is determined by the constant IMAGE_FORMAT.
*
* @author Michael Kölling and David J. Barnes.
* @version 2.0
*/
public class ImageFileManager
{
// A constant for the image format that this writer uses for writing.
// Available formats are "jpg" and "png".
private static final String IMAGE_FORMAT = "jpg";
/**
* Read an image file from disk and return it as an image. This method
* can read JPG and PNG file formats. In case of any problem (e.g the file
* does not exist, is in an undecodable format, or any other read error)
* this method returns null.
*
* @param imageFile The image file to be loaded.
* @return The image object or null is it could not be read.
*/
public static OFImage loadImage(File imageFile)
{
try {
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(imageFile);
if(image == null || (image.getWidth(null) < 0)) {
// we could not load the image - probably invalid file format
return null;
}
return new OFImage(image);
}
catch(IOException exc) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* Write an image file to disk. The file format is JPG. In case of any
* problem the method just silently returns.
*
* @param image The image to be saved.
* @param file The file to save to.
*/
public static void saveImage(OFImage image, File file)
{
try {
ImageIO.write(image, IMAGE_FORMAT, file);
}
catch(IOException exc) {
return;
}
}
}
D)HistoryManager
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class HistoryManager {
private ArrayList<OFImage> history;
private int currentStep;
public HistoryManager() {
history=new ArrayList<OFImage>();
}
public void add(OFImage image){
OFImage img=new OFImage(image);
if(history.size()==0){
currentStep=0;
history.add(img);
return;
}
if((currentStep+1)<=history.size())
history.subList(currentStep+1, history.size()).clear();
history.add(img);
currentStep=currentStep+1;
}
public OFImage getCurrentVersion(){
return history.get(currentStep);
}
public Boolean canUndo(){
if (currentStep>0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public Boolean canRedo(){
if (currentStep<(history.size()-1))
return true;
else
return false;
}
public void redo(){
if (canRedo())
currentStep=currentStep+1;
}
public void undo(){
if (canUndo())
currentStep=currentStep-1;
}
public void eraseAll(){
history.clear();
}
public int getCurrentStep(){
return currentStep;
}
public int getHistorySize(){
return history.size();
}
}
E) Filter
/**
* Filter is an abstract superclass for all image filters in this
* application. Filters can be applied to OFImages by invoking the apply
* method.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public abstract class Filter
{
private String name;
/**
* Create a new filter with a given name.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public Filter(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
/**
* Return the name of this filter.
*
* @return The name of this filter.
*/
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public abstract void apply(OFImage image);
}
F)ThresholdFilter
import java.awt.Color;
/**
* An three-level gray-based threshold filter.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public class ThresholdFilter extends Filter
{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class ThresholdFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public ThresholdFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
Color pixel = image.getPixel(x, y);
int brightness = (pixel.getRed() + pixel.getBlue() + pixel.getGreen()) / 3;
if(brightness <= 85) {
image.setPixel(x, y, Color.BLACK);
}
else if(brightness <= 170) {
image.setPixel(x, y, Color.GRAY);
}
else {
image.setPixel(x, y, Color.WHITE);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* An image filter to make the image a bit darker.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public class DarkerFilter extends Filter
{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class DarkerFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public DarkerFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
image.setPixel(x, y, image.getPixel(x, y).darker());
}
}
}
}
import java.awt.Color;
/**
* An image filter to mirror (flip) the image horizontally.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public class MirrorFilter extends Filter
{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class MirrorFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public MirrorFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width / 2; x++) {
Color left = image.getPixel(x, y);
image.setPixel(x, y, image.getPixel(width - 1 - x, y));
image.setPixel(width - 1 - x, y, left);
}
}
}
}
/**
* An image filter to make the image a bit lighter.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
* @version 1.0
*/
public class LighterFilter extends Filter
{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class LighterFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public LighterFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
image.setPixel(x, y, image.getPixel(x, y).brighter());
}
}
}
}
import java.awt.Color;
/**
* An image filter to mirror (flip) the image horizontally.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FlipVerticallyFilter extends Filter{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class MirrorFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public FlipVerticallyFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for(int y = 0; y < height / 2; y++) {
Color up = image.getPixel(x, y);
image.setPixel(x, y, image.getPixel(x,height - 1 - y));
image.setPixel(x,height - 1 - y,up);
}
}
}
}
import java.awt.Color;
/**
* An image filter to invert colors.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public class InvertFilter extends Filter
{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class InvertFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public InvertFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
Color pix = image.getPixel(x, y);
image.setPixel(x, y, new Color(255 - pix.getRed(),
255 - pix.getGreen(),
255 - pix.getBlue()));
}
}
}
}
import java.awt.Color;
/**
* An image filter to remove color from an image.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public class GrayScaleFilter extends Filter
{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class GrayScaleFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public GrayScaleFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
Color pix = image.getPixel(x, y);
int avg = (pix.getRed() + pix.getGreen() + pix.getBlue()) / 3;
image.setPixel(x, y, new Color(avg, avg, avg));
}
}
}
}
M) SmoothFilter
import java.awt.Color;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* An image filter to reduce sharp edges and pixelization. A bit like
* a soft lens.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public class SmoothFilter extends Filter
{
private OFImage original;
private int width;
private int height;
/**
* Constructor for objects of class SmoothFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public SmoothFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
original = new OFImage(image);
width = original.getWidth();
height = original.getHeight();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
image.setPixel(x, y, smooth(x, y));
}
}
}
/**
* Return a new color that is the smoothed color of a given
* position. The "smoothed color" is the color value that is the
* average of this pixel and all the adjacent pixels.
* @param xpos The xposition of the pixel.
* @param ypos The yposition of the pixel.
* @return The smoothed color.
*/
private Color smooth(int xpos, int ypos)
{
List<Color> pixels = new ArrayList<Color>(9);
for(int y = ypos - 1; y <= ypos + 1; y++) {
for(int x = xpos - 1; x <= xpos + 1; x++) {
if( x >= 0 && x < width && y >= 0 && y < height )
pixels.add(original.getPixel(x, y));
}
}
return new Color(avgRed(pixels), avgGreen(pixels), avgBlue(pixels));
}
/**
* @param pixels The list of pixels.
* @return The average of all the red values in the given list of pixels.
*/
private int avgRed(List<Color> pixels)
{
int total = 0;
for(Color color : pixels) {
total += color.getRed();
}
return total / pixels.size();
}
/**
* @param pixels The list of pixels.
* @return The average of all the green values in the given list of pixels.
*/
private int avgGreen(List<Color> pixels)
{
int total = 0;
for(Color color : pixels) {
total += color.getGreen();
}
return total / pixels.size();
}
/**
* @param pixels The list of pixels.
* @return The average of all the blue values in the given list of pixels.
*/
private int avgBlue(List<Color> pixels)
{
int total = 0;
for(Color color : pixels) {
total += color.getBlue();
}
return total / pixels.size();
}
}
import java.awt.Color;
/**
* An image filter to create a solarization effect.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
* @version 1.0
*/
public class SolarizeFilter extends Filter
{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class Solarize.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public SolarizeFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
Color pix = image.getPixel(x, y);
int red = pix.getRed();
if(red <= 127) {
red = 255 - red;
}
int green = pix.getGreen();
if(green <= 127) {
green = 255 - green;
}
int blue = pix.getBlue();
if(blue <= 127) {
blue = 255 - blue;
}
image.setPixel(x, y, new Color(red, green, blue));
}
}
}
}
O)EdgeFilter
import java.awt.Color;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* An image filter to detect edges and highlight them, a bit like
* a colored pencil drawing.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
*/
public class EdgeFilter extends Filter
{
private static final int TOLERANCE = 20;
private OFImage original;
private int width;
private int height;
/**
* Constructor for objects of class EdgeFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public EdgeFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
original = new OFImage(image);
width = original.getWidth();
height = original.getHeight();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
image.setPixel(x, y, edge(x, y));
}
}
}
/**
* Return a new color that is the smoothed color of a given
* position. The "smoothed color" is the color value that is the
* average of this pixel and all the adjacent pixels.
* @param xpos The x position of the pixel.
* @param ypos The y position of the pixel.
* @return The smoothed color.
*/
private Color edge(int xpos, int ypos)
{
List<Color> pixels = new ArrayList<Color>(9);
for(int y = ypos-1; y <= ypos+1; y++) {
for(int x = xpos-1; x <= xpos+1; x++) {
if( x >= 0 && x < width && y >= 0 && y < height ) {
pixels.add(original.getPixel(x, y));
}
}
}
return new Color(255 - diffRed(pixels), 255 - diffGreen(pixels), 255 - diffBlue(pixels));
}
/**
* @param pixels The list of pixels to be averaged.
* @return The average of all the red values in the given list of pixels.
*/
private int diffRed(List<Color> pixels)
{
int max = 0;
int min = 255;
for(Color color : pixels) {
int val = color.getRed();
if(val > max) {
max = val;
}
if(val < min) {
min = val;
}
}
int difference = max - min - TOLERANCE;
if(difference < 0) {
difference = 0;
}
return difference;
}
/**
* @param pixels The list of pixels to be averaged.
* @return The average of all the green values in the given list of pixels.
*/
private int diffGreen(List<Color> pixels)
{
int max = 0;
int min = 255;
for(Color color : pixels) {
int val = color.getGreen();
if(val > max) {
max = val;
}
if(val < min) {
min = val;
}
}
int difference = max - min - TOLERANCE;
if(difference < 0) {
difference = 0;
}
return difference;
}
/**
* @param pixels The list of pixels to be averaged.
* @return The average of all the blue values in the given list of pixels.
*/
private int diffBlue(List<Color> pixels)
{
int max = 0;
int min = 255;
for(Color color : pixels) {
int val = color.getBlue();
if(val > max) {
max = val;
}
if(val < min) {
min = val;
}
}
int difference = max - min - TOLERANCE;
if(difference < 0) {
difference = 0;
}
return difference;
}
}
P) PixelizeFilter
import java.awt.Color;
/**
* An image filter to create a pixelization effect, like an enlarged
* low-resolution digital image.
*
* @author Muhammad Naufal Refadi
* @version 1.0
*/
public class PixelizeFilter extends Filter
{
/**
* Constructor for objects of class PixelizeFilter.
* @param name The name of the filter.
*/
public PixelizeFilter(String name)
{
super(name);
}
/**
* Apply this filter to an image.
*
* @param image The image to be changed by this filter.
*/
public void apply(OFImage image)
{
final int PIXEL_SIZE = 5;
int width = image.getWidth();
int height = image.getHeight();
for(int y = 0; y < height; y += PIXEL_SIZE) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x += PIXEL_SIZE) {
Color pix = image.getPixel(x, y);
for(int dy = y; dy < y + PIXEL_SIZE; dy++) {
for(int dx = x; dx < x + PIXEL_SIZE; dx++) {
if( dx < width && dy < height )
image.setPixel(dx, dy, pix);
}
}
}
}
}
}
Dan berikut hasilnya